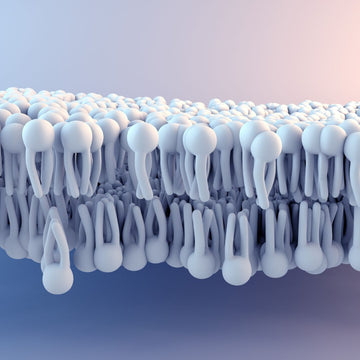
Plasmalogens are critical membrane components involved with neurotransmitter release. They are found in high concentrations in the brain and heart. However, they are made mainly in the liver, and there are no adequate food sources. As a result, levels dramatically decrease after age 60. They are essential to nerve cells and help cells communicate and function. Several scientific studies show plasmalogen levels are low in people with neurodegenerative diseases, including dementia, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis. Plasmalogen levels are also low in pancreatic cancer, diabetes, and heart and stroke.
Plasmalogens also have antioxidant properties – some plasmalogens contain oleic acid, a mono-unsaturated fatty acid found in olive oil, and some contain polyunsaturated fatty acids like docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which is essential for health. DHA (an omega-3 found in fish oils) promotes cardiovascular health, is required for optimal brain function, is needed for cells to function, and is anti-inflammatory.